Preparation of master plan starts with base map preparation before which relevant data of all
the necessary information, which is to be presented via base, map is collected. For base map
preparation, National Urban Information System (NUIS) Scheme has prepared maps on
1:10,000 scale and made available on NRSC/ISRO Geoportal Bhuvan for Urban Local Bodies
for 152 towns. Bhuvan NUIS GIS database comprises
1)Base layers
Road, Rail, Canal, Transportation nodes, Drainage, Surface water Bodies.
2)Thematic layers
Urban Land use / Cover, Geomorphology, Lithology, Geological
structures, Physiography
3)Administrative Layers
State, District, Village, City/Town boundaries and Ward
Boundaries.
Attribute data has spatial layers as, administrative boundaries, forest boundary, settlement and
village locations / names and city / town boundaries and non‐spatial data. Other sources of
licensed/authentic versions of interpreted satellite imageries can also be used for preparation
of base map.
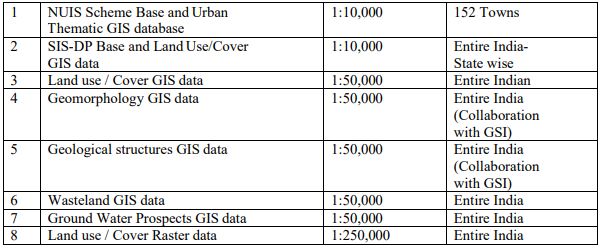
The Thematic GIS databases available on Bhuvan range from a scale of 1:10,000, to 1:250,000.
The important Satellite data and thematic GIS data resources available for utilization for
various planning and development are listed below.
Table Bhuvan Satellite data and thematic GIS data resources available
Table Base and Thematic GIS data services
Once the base and thematic layers from the satellite imagery are prepared, other city/town
specific information such as, cadastral maps, revenue records, and plans of government
agencies and attribute information from Industrial Development Corporations, Public Work
Department, Railways, National Highway Authority could be integrated for preparation
comprehensive GIS database as required for development plan/ master plan preparation.
The satellite imageries, Resources at LISS‐4 and Cartosat PAN, can be overlaid on cadastral
maps to prepare base map. These satellite images depict field bunds, cart tracks, settlements,
tanks and other cultural features like roads, railway network and canals. These features
facilitate identification of Ground Control Points (GCP) for tie down satellite image and
cadastral map. For overlaying cadastral map with satellite image it is required that cadastral
map be generated in vector mode. In this process the main tasks are acquisition of cadastral
maps, scanning and digitization of cadastral maps and generation of vector data. Once the
cadastral maps in vector mode are available, the geo‐referencing of these maps can be done.
The geo‐referencing of digital cadastral maps and overlaying with satellite image consists of
the following steps:
- Acquisition of GCP’s
- Transformation model development and assessment
- Geo‐referencing of cadastral maps
- Validation of Geo‐referenced map, in isolation
- Validation of Geo‐referenced map, with neighbourhood
- Mosaic generation at Revenue Inspector (RI), Taluk and district level
Good planning and engineering practice dictate the preparation of large-scale maps as a basis
for sound community development and redevelopment. In urban areas. and particularly ingrowing urban areas, such large scale maps are currently being compiled at an unprecedented
rate by photogrammetric methods. Relatively simple changes in the specifications governing
these photogrammetric mapping operations can make the resulting maps not only more
effective planning and engineering tools but can, at relatively little additional cost, lay the
foundation for the eventual creation of a multipurpose cadastre.
Design of the base mapping data content and structure must be flexible enough to allow a
variety of users to relate the cadastral parcels to specific types of base information. This
objective can readily be achieved by creating and maintaining the base mapping data in a
coordinated series of different levels or overlays. Photographic and orthophotographic base
maps at a minimum contain the complete photographic image of the terrain surface covered to
which other levels or overlays may be added to create the complete base map. The primary
base map datum is the geodetic reference framework used to establish the location of all other
features. The following reference systems are in current use throughout the United States:
- Geographic Coordinates (latitude and longitude)
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) rectangular coordinates
- State Plane Coordinates
Geographic coordinates provide the principal system used for computation of geodetic control
point positions. The UTM rectangular coordinate system is a metric worldwide system of
predominate use in federal mapping environments. State plane coordinates are most commonly
used at the state and local levels, currently defined in English units but with metric units also
widely available. Because of the greater familiarity with their use at the local level, State Plane
Coordinates are normally used as the geodetic reference framework in current implementation
projects and are recommended for local multipurpose cadastres.